AVDECC ISE Amsterdam 2014 Presentation
AVB Bandwidth Calculator for Numbers V2.5
Download Link
Changes
- Support for 192 kHz added.
Details
For the very detailed explanations of the contents of an AVB Audio Ethernet frame, see the Maximum AVB Channel Counts presentation.
Maximum AVB Channel Counts
The breakdown of all of the ethernet frame timing is discussed, and the maximum channel counts for 100baseT and gigE physical layer are calculated for both 48 kHz and 96 kHz AVB streams using AVTP subtype 0 ( iec61883-6 AM824 ) encoding.
AVDECC AES NY 2013 Presentation
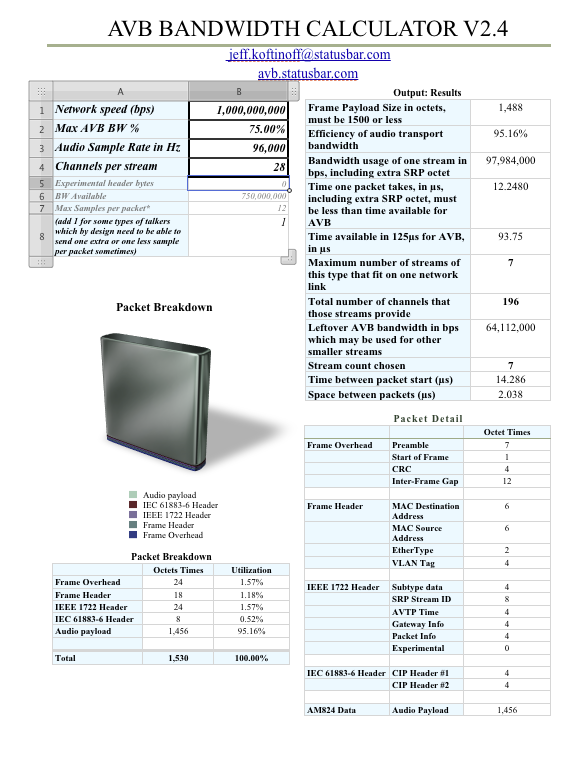
AVB Bandwidth Calculator for Numbers V2.4
Download Link
Changes
- Fixed '(add 1 for some types of talkers which by design need to be able to send one extra or one less sample per packet sometimes)' field, and defaults to 1.
Details
For the very detailed explanations of the contents of an AVB Audio Ethernet frame, see the Maximum AVB Channel Counts presentation.
Getting Started
- Familiarize yourself with the standards, the General FAQ, and the Developer FAQ.
- Review the Technical Papers from the Knowledge Center from AVnu - Specifically start with AVB Software Interfaces and Endpoint Architecture Guidelines
IEEE 1722.1 Protocol Features
Overview
IEEE 1722.1 provides the Audio Video Discovery, Enumeration, Connection management, and Control (AVDECC) protocol for AVB devices.
Discovery
- Advertising
- Querying (Global and Specific)
- Support for redundant networks
Enumeration and Control
- Describe the internal structure of the device from the stream entry/exit through to the "physical" entry/exit
- Describe the internal structure within the different limitations of the device (channel limits at different sample rates, etc)
- Describe the internal latency through the device from the defined timing reference plane to the "physical" world (or the define latency from reference plane to reference plane via the DSP)
- Describes and controls the clocking model within the device to configure media clocking sources, sample rate converters, etc.
- Describe the AVB capabilities of the interfaces and provide the current AVB related information (802.1AS GMID, MSRP domain) for each AVB interface
- Describe and control the mapping of media sources and sinks to channels within the stream sinks and sources
- Describe and control the signal chains (DSP, mute, volume, mixers, selectors, etc) through the device
- Provide user settable names for many objects within the device including stream, media sources and sinks (jacks), controls, etc
- Describe and control generic control points within the device (location information, enables, video camera controls, etc)
- Perform key management for securing the network
- Perform basic authentication of controllers
- Enable and disable transport and stream security
- Distributes updates to interested controllers
- Provides diagnostic information such as avb interface event counters and errors, stream packet event counters and errors, and clock domain lock status, as well as vendor specific counters when necessary.
- Transport AVC protocol, HDCP IIA key exchange protocol, and vendor specific protocols.
Connection Management
- Connection/disconnection of streams
- Persistent connections
- Status query for both AVDECC Listeners and AVDECC Talkers
- Transport of relevant SRP data
IEEE 1722.1 Protocol Features
Overview
IEEE 1722.1 provides the Audio Video Discovery, Enumeration, Connection management, and Control (AVDECC) protocol for AVB devices.
Discovery
- Advertising
- Querying (Global and Specific)
- Support for redundant networks
Enumeration and Control
- Describe the internal structure of the device from the stream entry/exit through to the "physical" entry/exit
- Describe the internal structure within the different limitations of the device (channel limits at different sample rates, etc)
- Describe the internal latency through the device from the defined timing reference plane to the "physical" world (or the define latency from reference plane to reference plane via the DSP)
- Describes and controls the clocking model within the device to configure media clocking sources, sample rate converters, etc.
- Describe the AVB capabilities of the interfaces and provide the current AVB related information (802.1AS GMID, MSRP domain) for each AVB interface
- Describe and control the mapping of media sources and sinks to channels within the stream sinks and sources
- Describe and control the signal chains (DSP, mute, volume, mixers, selectors, etc) through the device
- Provide user settable names for many objects within the device including stream, media sources and sinks (jacks), controls, etc
- Describe and control generic control points within the device (location information, enables, video camera controls, etc)
- Perform key management for securing the network
- Perform basic authentication of controllers
- Enable and disable transport and stream security
- Distributes updates to interested controllers
- Provides diagnostic information such as avb interface event counters and errors, stream packet event counters and errors, and clock domain lock status, as well as vendor specific counters when necessary.
- Transport AVC protocol, HDCP IIA key exchange protocol, and vendor specific protocols.
Connection Management
- Connection/disconnection of streams
- Persistent connections
- Status query for both AVDECC Listeners and AVDECC Talkers
- Transport of relevant SRP data
Rebuilt site
Rebuilt this site with the Nikola tool.